Why do learning outcomes matter?
Learning outcomes facilitate College of Marin’s mission to provide aligned and transparent coursework organized toward an achievable degree or certificate. Students should know what they will learn by the end of the course and faculty should know be clear about what they are teaching and what they want students to learn by the end of the course.
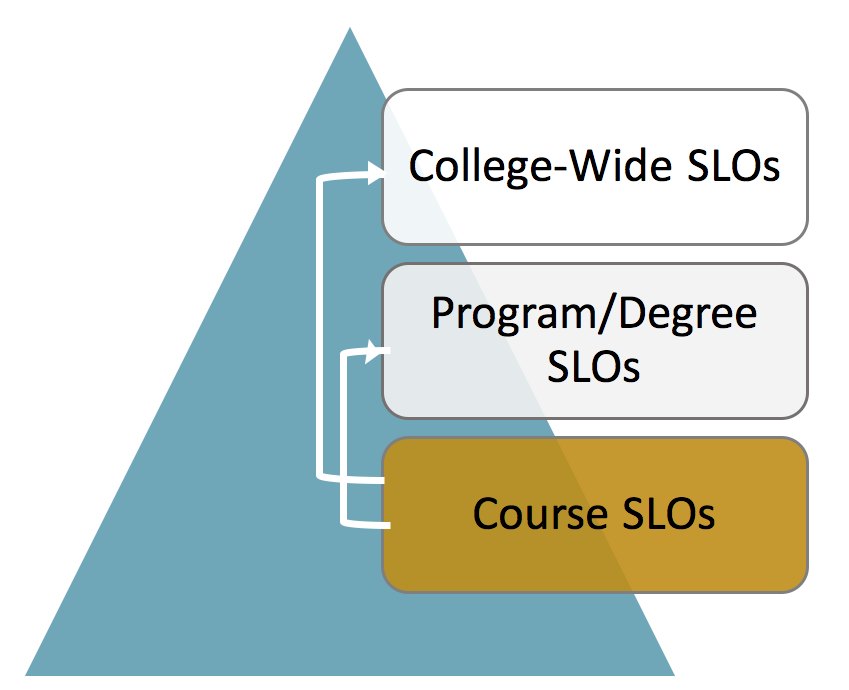
College Wide or Institutional Learning Outcomes (ILOs or ISLOs)
ILOs represent broad categories of competencies. Students achieve outcomes, regardless of academic program of study, upon completion of College of Marin’s certificate or degree programs.
Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs or PSLOs)
PLOs are the knowledgeor skills that students achieve upon completion of their academic program.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs or CSLOs)
CLOs are the overarching knowledge or skills that students achieve upon completion of a course.
What constitutes a program?
A program is defined as “an organized sequence of courses leading to a defined objective, a degree, a certificate, a diploma, a license, or transfer to another institution of higher education” by Title 5, § 55000.
What is the difference between program goals and learning objectives?
The terms are often used interchangeably, but they do have distinct differences. Program goals are long-term, broad statements of what students should learn, understand, value, and appreciate as a result of completing a program, and goals should directly relate to a mission statement. Conversely, learning objectives are short-term, precise statements that describe what faculty plan on covering in a learning experience. While program goals may be difficult or impracticable to measure, learning objectives are observable and measurable. Multiple learning objectives are typically developed to reach one program goal.
How to create a Course Level Outcome or CLO
Your department chair has asked you to update the course outline of record for a class you regularly teach. This is an opportunity to share your knowledge of the materials and method of teaching. To begin, ask yourself: as an instructor preparing to teach my course, what do I want my students to learn? Make a list. These are your CLOs. Then use the checklist below to make sure the CLOs are brand enough and measurable.
- Does the outcome reflect the overall course topics?
- Does the outcome describe what the program intends for students to know (cognitive), think (affective, attitudinal), or do (behavioral, performance)?
- Is the outcome important/worthwhile?
- Simple and specific?
- Measurable?
- A result of learning planned for the class?
- Easily communicated to others?
- Do you have or can you create an activity to enable students to learn the desired outcome? If so, describe that activity and make sure it finds its way into your syllabus.
- Are the number of outcomes reasonable? (How many?)
- Can the outcome be used to make decisions on how to improve the program?
If you answered yes to each item, you’ve written solid CLOs. Congratulations, you’ve helped establish the foundation for aligning courses to programs and to our institution making it easier for students to visualize their way to a degree or certificate. You also made yourself and your colleagues more effective instructors.
To find SLOs for course syllabi: Up-to-date SLOs from eLUMEN can be viewed via the link: https://marin.elumenapp.com/public/ Please remember to click on the blue "Course Outline of Record" in the 3rd column to view SLOs.
SLO Assessment Schedules: All courses are assessed every other year
Beginning in fall 2023, COM will assess all courses and all sections of all courses every other year, followed by a year to analyze SLO data. SLO data collected one year will be analyzed the following year. Accordingly, we will assess in Fall 2023 and Spring 2024, and analyze the data in Fall 25 and Spring 26.
The old assessments schedule shown below are no longer used and are superseded by the new Improvement Plan in which all courses are assessed every other year.
- Dental Assisting
- Fire Technology
- Medical Assisting
- Anthropology
- Behavioral Sciences
- Psychology
- Sociology)
- Business
- Hospitality
- Real Estate
- Statistics
- Vocational - Hospitality
- Administration of Justice
- Auto Collision Repair Technology
- Automotive Repair Technology
- Bus Operator Apprenticeship Program
- Computer Information Systems
- Court Reporting
- Electronics Technology
- Education
- Graphic Design
- Machine Metals Technology
- Multimedia Studies
- Vocational - Construction
- Welding
- Counseling
- Education
- Study Skills
- Work Experience
- Communication/Film Video
- Film
- Humanities
- Journalism
English as a Second Language ESL(N)
- Foundational Skills
- Summer Foundational Skills
- Focused Skills
English / Humanities / Philosophy
Health Education, Kinesiology, Athletics
Health Sciences
- Biology
- Environmental Science
- Geography
- Geology
- Dance
- Drama
- Music
- Astronomy
- Chemistry
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Physics
- Economics
- Ethnic Studies
- History
- Political Science
- Social Science
